Dry etching, as a core technology in the field of micro- and nano-fabrication, is widely applied in integrated circuit (IC) manufacturing and micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) due to its advantages of high precision and anisotropy. Its fundamental principle involves achieving precise etching by facilitating physical or chemical reactions between gases or plasmas and the material surface. In this process, the design of the Showerhead (also known as a gas shower head, gas distributor plate, or gas dispersion plate) directly determines the uniformity of gas distribution and the stability of the etching process.
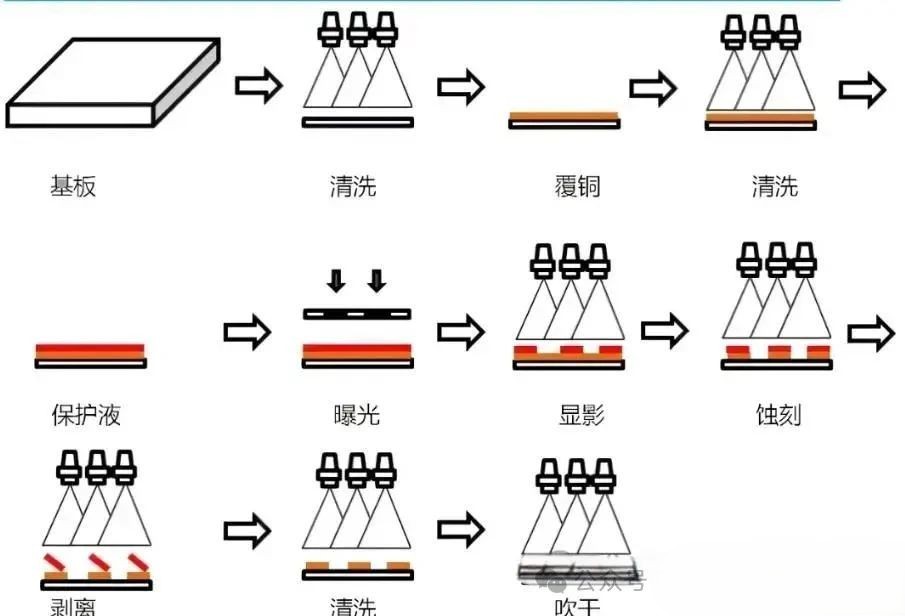
Definition of Etching
Etching is a crucial process technology in the field of micro- and nano-fabrication. By precisely manipulating chemical or physical means, it can accurately remove material from specific regions on the surface, thereby creating the desired microstructures or patterns. Its basic principles encompass a wide variety of physical and chemical processes aimed at altering or stripping one or more layers of material from the surface.
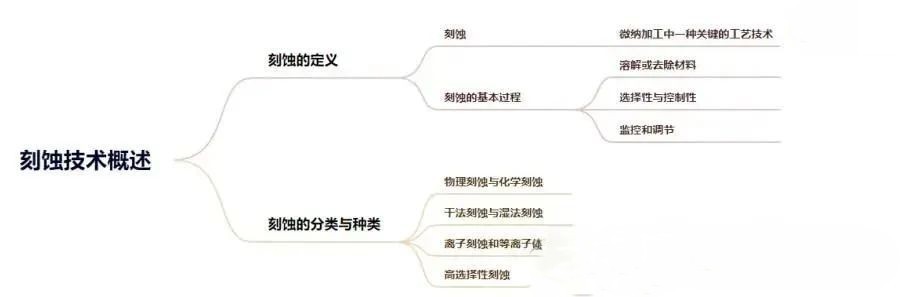
Key Steps in the Basic Etching Process
01 Dissolving or Removing Material
The core objective of etching is to precisely remove or transform atoms or molecules from specific regions on the material surface. This can be achieved through dissolution induced by chemical reactions, such as when certain solutions react with the material surface through oxidation-reduction or other reactions, gradually dissolving the material. Alternatively, physical processes like ion bombardment can be employed, where high-speed ions strike the material surface, sputtering out atoms, or laser irradiation can be used to modify the surface structure of the material by applying high-energy light beams, thereby achieving material removal or modification.
02 Selectivity and Control
The etching process must exhibit a high degree of selectivity to ensure that etching occurs only in predetermined specific regions while leaving other areas completely unaffected. Simultaneously, precise control over the etching rate, the final structural morphology, and surface roughness is of paramount importance. An excessively fast or slow etching rate can affect the precision and quality of the structures. The structural morphology must strictly conform to design requirements, and surface roughness directly impacts device performance and reliability.
03 Monitoring and Adjustment
Real-time monitoring and precise adjustment are indispensable during the etching process. By utilizing advanced monitoring equipment and techniques, real-time information on various parameters during etching, such as etching depth and rate, can be obtained. Based on this feedback, etching conditions can be promptly adjusted to ensure that the desired structures or patterns are accurately replicated.
Classification and Types of Etching
Etching techniques can be subdivided into various types based on their working principles, the form of energy used, or the type of solvent employed. Each type demonstrates unique advantages in specific application scenarios.
Physical Etching vs. Chemical Etching
Physical Etching: This etching method primarily relies on physical energy, such as ion bombardment or lasers, to directly remove material from the surface. For example, ion beam etching (IBE) uses a precisely controlled ion beam to perform accurate directional bombardment on the material surface. The ion beam acts like a microscopic "scalpel," gradually stripping atoms from the material surface layer by layer, enabling precise etching of materials and offering significant advantages in fabricating high-precision microstructures.
Chemical Etching: In contrast to physical etching, chemical etching depends on chemical reactions in solutions to remove material from the surface. Wet etching is a typical representative of chemical etching, where materials are immersed in specific solutions, and chemical substances in the solution react with the material surface to selectively dissolve or remove specific parts of the material. This method is widely used in scenarios involving large-area materials or where high etching selectivity is required.
Dry Etching vs. Wet Etching
Dry Etching: Dry etching is an etching process carried out in an environment without liquid phases. Typically, it uses gases (such as hydrogen fluoride) or plasmas to interact with the material surface, achieving material removal. Dry etching offers advantages such as high etching precision and good anisotropy, enabling fine-structure processing at the micro- and nano-scale. It is extensively applied in high-end fields like IC manufacturing.
Wet Etching: Wet etching is an etching process conducted in a liquid environment, relying on the chemical action of corrosive solutions to dissolve or remove material from the surface. This method is relatively simple to operate and cost-effective, suitable for situations where the etching precision requirements are not extremely high but large-area materials need to be processed, such as in the etching of simple metal patterns.
Ion Etching and Plasma Etching
Ion Etching: Ion etching removes material by using an ion beam to strike the material surface, imparting sufficient energy to the surface atoms to cause them to detach from the material body. This approach provides extremely high selectivity and precise control capabilities, making it particularly suitable for fabricating microstructures with extremely high precision requirements, such as the micro- and nano-structure processing of optical components.
Plasma Etching: Plasma etching takes place in a plasma environment, utilizing ions or high-energy particles to etch the material surface. The plasma contains a large number of active ions, free radicals, and other particles that can undergo complex physical and chemical reactions with the material surface, thereby achieving material etching. This method offers unique advantages in producing complex micro- and nanostructures and is commonly used in the processing of complex circuit structures in semiconductor chip manufacturing.
High-Selectivity Etching
High-selectivity etching is a highly specialized etching method that can precisely and selectively remove specific materials without damaging other regions. It plays a crucial role in fabricating microstructures, integrated circuits, and MEMS. For instance, in IC manufacturing, etching between different material layers requires a high degree of selectivity to ensure that when removing one layer of material, no damage is caused to other layers, thereby guaranteeing chip performance and reliability.
Each etching type has its own unique advantages and limitations. In practical applications, selecting the appropriate etching technique requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors, including the characteristics of the material being prepared, the required dimensional and shape precision of the structures, surface quality requirements, and specific needs of the particular application. Therefore, in different process flows, a single etching method may be employed, or multiple etching methods may be cleverly combined to achieve the best processing results.
AMTD provides high-precision Showerhead services for core components. Its products mainly include Shower head, Face plate, Blocker Plate, Top Plate, Shield, Liner, pumping ring, Edge Ring, and other core semiconductor equipment parts. These products are widely used in fields such as semiconductors and display panels, boasting excellent performance and high market recognition.
Source: Dry Etching - ICP-CCP Official Account







